Introduction
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are at the forefront of global discussions on climate change. These emissions, primarily consisting of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), arise from various human activities and significantly contribute to global warming. This article delves into the different categories of GHG emissions and discusses their impacts and reduction strategies.
What are GHG Emissions?
GHG emissions refer to gases that trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to the greenhouse effect. The most common greenhouse gases include CO2, resulting from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes; methane, emitted during the production and transport of coal, oil, and natural gas, and by livestock and other agricultural practices; and nitrous oxide, released from agricultural and industrial activities, as well as combustion of fossil fuels and solid waste. These emissions are pivotal in understanding and addressing climate change.
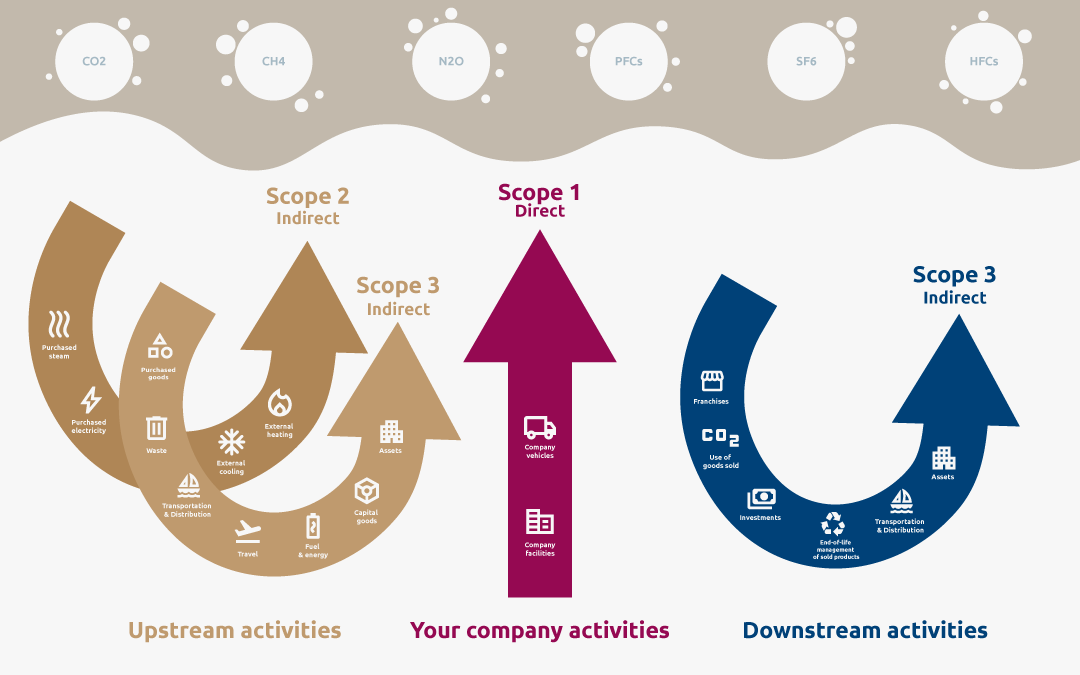
Scope 1: Direct Emissions
Scope 1 emissions are direct GHG emissions that occur from sources owned or controlled by an organization. This includes emissions from combustion in boilers, furnaces, vehicles, and chemical production in owned or controlled facilities. Reducing Scope 1 emissions can be achieved through measures such as improving energy efficiency, using cleaner fuels, and investing in renewable energy sources.
Scope 2: Indirect Emissions from Energy Purchases
Scope 2 covers indirect GHG emissions from the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling consumed by an organization. These emissions occur at the facility where the energy is generated. Companies can reduce Scope 2 emissions by purchasing green energy, improving building energy efficiency, and investing in on-site renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines.
Scope 3: All Other Indirect Emissions
Scope 3 encompasses all other indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain, including both upstream and downstream emissions. This includes the extraction and production of purchased materials, transportation of purchased fuels, and use of sold products and services. Addressing Scope 3 emissions involves engaging with suppliers for more sustainable practices, redesigning products to be more energy-efficient, and encouraging consumers to use products more sustainably.
The Importance of Emission Measurement and Reporting
Accurately measuring and reporting GHG emissions across all scopes is vital for understanding a company’s full environmental impact. These reports are crucial not only for the companies themselves in managing their carbon footprint but also for stakeholders and the general public. They foster transparency and are integral to global efforts in reducing emissions.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing GHG emissions across all three scopes is critical in comprehensively tackling an organization’s environmental impact. Conscious actions and continuous research play a significant role in contributing to the reduction of GHG emissions and combating climate change.
